
A peripheral angiogram is a key diagnostic test for identifying blocked or narrowed arteries in the limbs.
A peripheral angiogram is a diagnostic test used to examine blood flow in the arteries outside the heart—typically in the legs, arms, and other peripheral areas. It helps detect blockages that may lead to serious conditions like peripheral artery disease (PAD). The test involves injecting contrast dye into the arteries and taking detailed X-ray images.
A peripheral angiogram is a minimally invasive imaging test used to examine the arteries that supply blood to the arms, legs, kidneys, and other areas outside the heart. It helps detect narrowed, blocked, or abnormal arteries and plays a vital role in diagnosing peripheral artery disease (PAD).
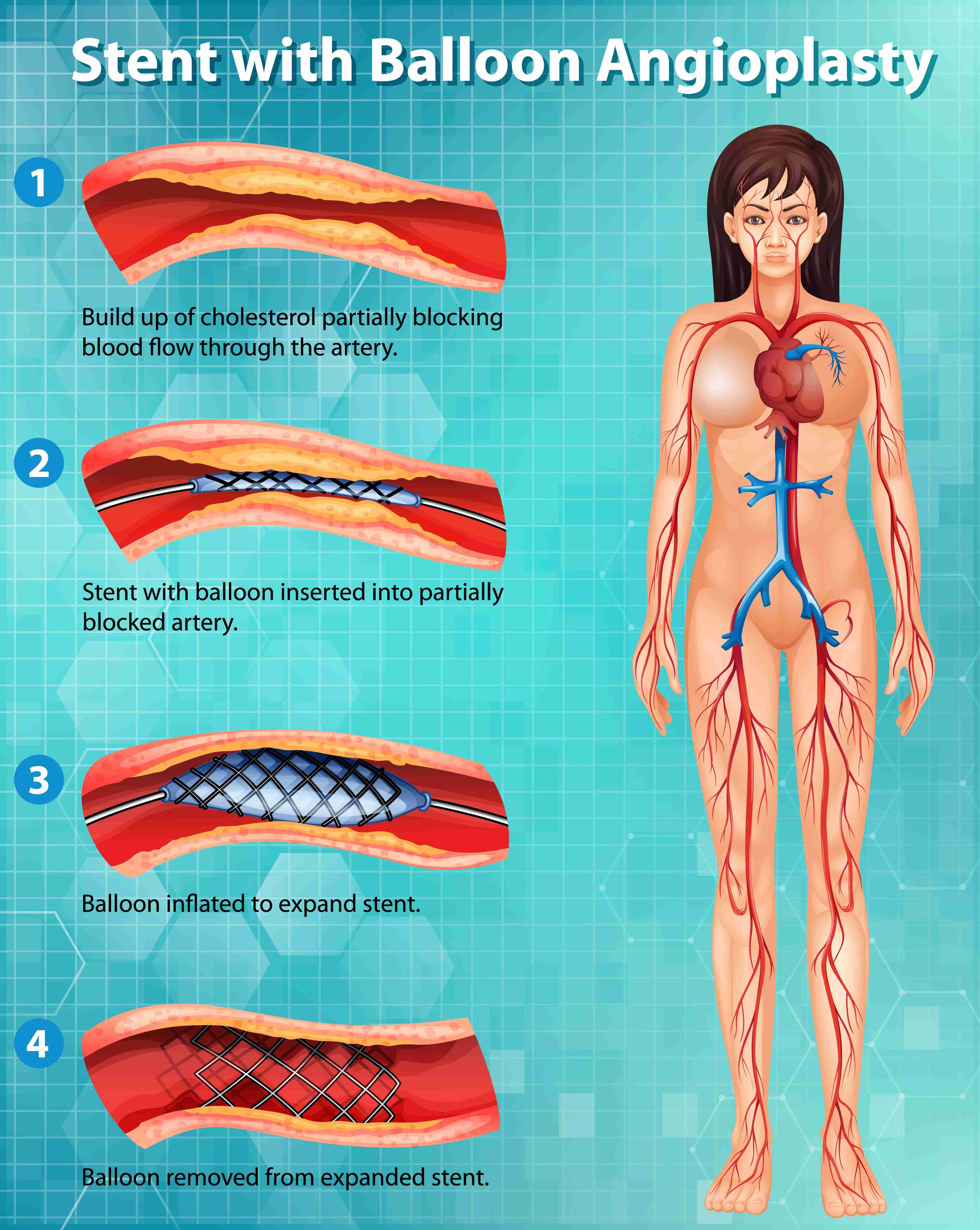
Diagram of stent with Balloon Angioplasty.
The test is usually done in a hospital catheterisation lab (cath lab) and takes about 30 minutes to an hour.
Step 1: Preparation
Step 2: Local Anaesthesia and Catheter Insertion
Step 3: Injection of Contrast Dye
Step 4: Image Analysis and Catheter Removal
Step 5: Recovery
A peripheral angiogram may be recommended if you have symptoms such as:
You may also need this test if you have risk factors for PAD, such as:
This test is generally safe, but possible complications include:
Always discuss pre-existing conditions and medications with your doctor before undergoing the test.
If you notice symptoms such as persistent leg pain, numbness, slow-healing wounds, or discoloured skin, don’t ignore them. These could be early signs of circulatory problems that need medical attention.
A peripheral angiogram is a valuable test that helps detect circulation issues before they become serious. It plays a critical role in diagnosing and planning treatment for conditions like peripheral artery disease. If you're experiencing symptoms of poor circulation, early diagnosis can make a big difference in managing your health.
1. What are the benefits of a peripheral angiogram?
It helps detect narrowed or blocked arteries in your limbs, often before symptoms become severe. This early diagnosis supports timely treatment to prevent complications like ulcers or, in severe cases, limb loss.
2. What are the risks of a peripheral angiogram?
Minor risks include bruising or bleeding at the insertion site. Some may have an allergic reaction to the contrast dye. In rare instances, there could be a risk of blood vessel damage or clot formation.
3. Can an angiogram damage the kidneys?
Yes, the contrast dye used can affect kidney function, especially in people with pre-existing kidney issues or diabetes. Drinking plenty of fluids before and after the test usually helps flush the dye from your body.
4. Is there any danger in angiography?
It’s generally safe. Serious complications like artery damage or infection are rare. Your doctor will assess your overall health and take steps to ensure the procedure is as safe as possible.
We offer expert care across key specialties, including Medicine, Cardiology, Orthopaedics, ENT, Gynaecology, and more—delivering trusted treatment under one roof.

Dr. Rakesh
Prakash Hospital Pvt. Ltd. is a 100 bedded NABH NABL accredited multispecialty hospital along with a center of trauma and orthopedics. We are in the service of society since 2001.
OUR SPECIALITIES
Contact Us
D – 12A, 12B, Sector-33, G. B. Nagar, Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301
+91-8826000033

© 2025 All rights reserved.
Designed and Developed by Zarle Infotech